Connect With Us
Blog
Blog
How an Ankle Replacement Restores Mobility
Ankle replacement is a surgical procedure in which a damaged ankle joint is replaced with an artificial implant to restore function and reduce pain. The surgery is performed under anesthesia, allowing the surgeon to remove diseased or injured bone and cartilage before placing the prosthetic joint. Common causes that may lead to ankle replacement include severe arthritis, bone fractures, infections, and tumors that compromise joint integrity. Symptoms often include chronic pain, stiffness, and limited mobility that do not respond to conservative treatments. A podiatrist can evaluate ankle health, determine if replacement is appropriate, coordinate appropriate care and manage post-operative recovery. If you have an ankle condition, it is suggested that you consult a podiatrist who can determine if this type of foot surgery is right for you.
Foot surgery is sometimes necessary to treat a foot ailment. To learn more, contact Darlyne Cange, DPM of Cange Podiatry, DPM, PA. Our doctor will assist you with all of your foot and ankle needs.
When Is Surgery Necessary?
Foot and ankle surgery is generally reserved for cases in which less invasive, conservative procedures have failed to alleviate the problem. Some of the cases in which surgery may be necessary include:
- Removing foot deformities like bunions and bone spurs
- Severe arthritis that has caused bone issues
- Cosmetic reconstruction
What Types of Surgery Are There?
The type of surgery you receive will depend on the nature of the problem you have. Some of the possible surgeries include:
- Bunionectomy for painful bunions
- Surgical fusion for realignment of bones
- Neuropathy decompression surgery to treat nerve damage
Benefits of Surgery
Although surgery is usually a last resort, it can provide more complete pain relief compared to non-surgical methods and may allow you to finally resume full activity.
Surgical techniques have also become increasingly sophisticated. Techniques like endoscopic surgery allow for smaller incisions and faster recovery times.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our offices located in Glen Burnie and Ellicott City, MD . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Toenail Fungus Discomfort and Mental Well-Being

Toenail fungus is often dismissed as a cosmetic problem, but it can affect both physical comfort and emotional health. Thickened, brittle, or discolored nails may press against shoes, leading to irritation and pain with walking or standing. This ongoing discomfort can interfere with daily routines and limit physical activity. Many people also feel embarrassed by the appearance of infected nails, which may lead them to avoid open-toed shoes or social situations. Feeling self-conscious over time can quietly affect confidence and overall mental well-being. When left untreated, toenail fungus may worsen, making nails harder to trim and increasing discomfort. Addressing the problem early can improve both foot comfort and peace of mind. If toenail changes are causing pain, frustration, or emotional stress, it is suggested that you see a podiatrist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, which may include prescribed medication.
If left untreated, toenail fungus may spread to other toenails, skin, or even fingernails. If you suspect you have toenail fungus it is important to seek treatment right away. For more information about treatment, contact Darlyne Cange, DPM of Cange Podiatry, DPM, PA. Our doctor can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
Symptoms
- Warped or oddly shaped nails
- Yellowish nails
- Loose/separated nail
- Buildup of bits and pieces of nail fragments under the nail
- Brittle, broken, thickened nail
Treatment
If self-care strategies and over-the-counter medications does not help your fungus, your podiatrist may give you a prescription drug instead. Even if you find relief from your toenail fungus symptoms, you may experience a repeat infection in the future.
Prevention
In order to prevent getting toenail fungus in the future, you should always make sure to wash your feet with soap and water. After washing, it is important to dry your feet thoroughly especially in between the toes. When trimming your toenails, be sure to trim straight across instead of in a rounded shape. It is crucial not to cover up discolored nails with nail polish because that will prevent your nail from being able to “breathe”.
In some cases, surgical procedure may be needed to remove the toenail fungus. Consult with your podiatrist about the best treatment options for your case of toenail fungus.
If you have any questions please contact our offices located in Glen Burnie and Ellicott City, MD . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
Foot Anatomy and How It Supports Your Body
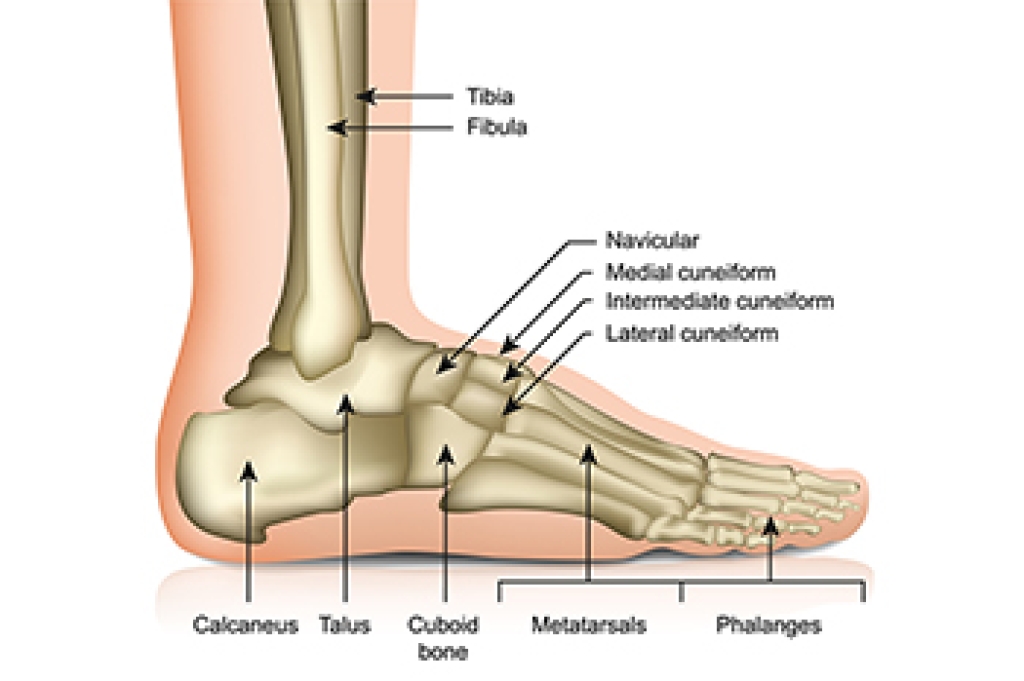
The complex structure of the foot is designed to support body weight and allow smooth movement while standing and walking. It contains 26 bones that work together to provide strength, balance, and flexibility. The tarsal bones form the rearfoot and ankle, creating a stable foundation, and help to absorb impact. The metatarsals make up the midfoot and act as supportive beams that distribute weight across the foot during standing and motion. Additionally, the phalanges are the toe bones, which assist with balance and push off during walking. When these bones are not functioning properly, pain and instability can occur. A podiatrist can evaluate foot anatomy, diagnose problems, and create treatment plans to restore proper function. If you have foot pain, it is suggested that you consult a podiatrist who can provide an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
If you have any concerns about your feet, contact Darlyne Cange, DPM from Cange Podiatry, DPM, PA. Our doctor can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
Biomechanics in Podiatry
Podiatric biomechanics is a particular sector of specialty podiatry with licensed practitioners who are trained to diagnose and treat conditions affecting the foot, ankle and lower leg. Biomechanics deals with the forces that act against the body, causing an interference with the biological structures. It focuses on the movement of the ankle, the foot and the forces that interact with them.
A History of Biomechanics
- Biomechanics dates back to the BC era in Egypt where evidence of professional foot care has been recorded.
- In 1974, biomechanics gained a higher profile from the studies of Merton Root, who claimed that by changing or controlling the forces between the ankle and the foot, corrections or conditions could be implemented to gain strength and coordination in the area.
Modern technological improvements are based on past theories and therapeutic processes that provide a better understanding of podiatric concepts for biomechanics. Computers can provide accurate information about the forces and patterns of the feet and lower legs.
Understanding biomechanics of the feet can help improve and eliminate pain, stopping further stress to the foot.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our offices located in Glen Burnie and Ellicott City, MD . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
Causes and Symptoms of Cuboid Syndrome
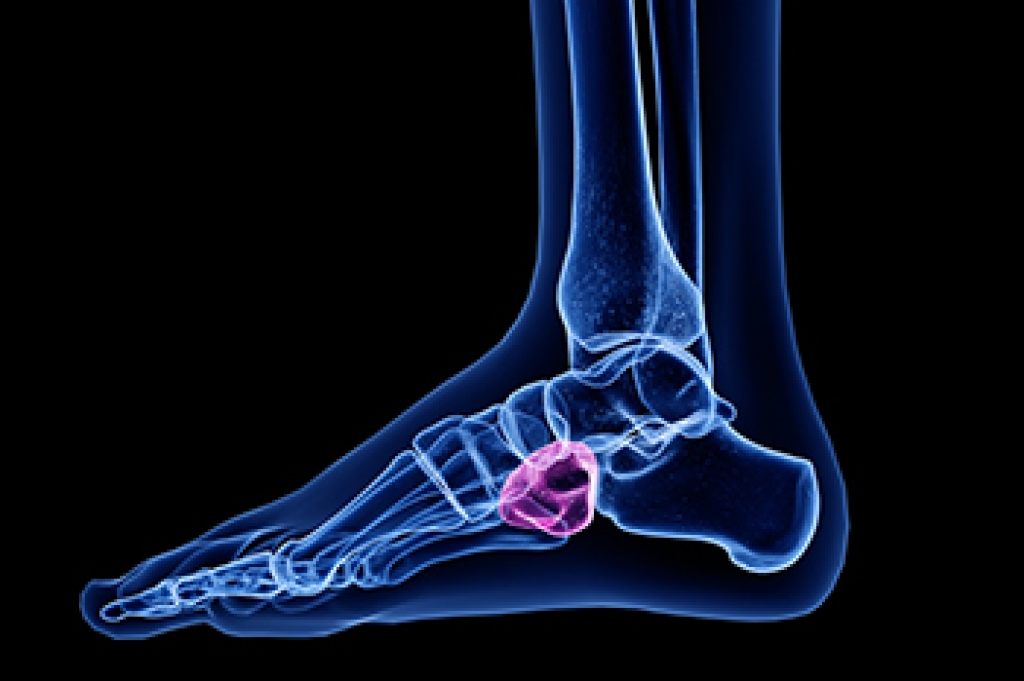
Cuboid syndrome is a foot condition that results from a subtle injury to the calcaneocuboid joint, on the outer side of the midfoot, where the heel bone meets the cuboid bone, and leading to pain along the outer side of the foot and difficulty with normal walking. It often develops after an ankle sprain, overuse, or repetitive strain that affects joint alignment and surrounding soft tissues. Common symptoms include pain, tenderness, swelling, and discomfort that worsens with weight-bearing activity. Risk factors include high impact sports, flat feet, wearing improper footwear, and previous foot or ankle injuries. A podiatrist can diagnose cuboid syndrome through clinical evaluation and restore joint alignment with manual techniques, along with recommending supportive footwear and orthotics. If you have pain on the outside of your foot, it is suggested that you consult a podiatrist to relieve discomfort and prevent ongoing instability.
Cuboid syndrome, also known as cuboid subluxation, occurs when the joints and ligaments near the cuboid bone in the foot become torn. If you have cuboid syndrome, consult with Darlyne Cange, DPM from Cange Podiatry, DPM, PA. Our doctor will assess your condition and provide you with quality foot and ankle treatment.
Cuboid syndrome is a common cause of lateral foot pain, which is pain on the outside of the foot. The condition may happen suddenly due to an ankle sprain, or it may develop slowly overtime from repetitive tension through the bone and surrounding structures.
Causes
The most common causes of cuboid syndrome include:
- Injury – The most common cause of this ailment is an ankle sprain.
- Repetitive Strain – Tension placed through the peroneus longus muscle from repetitive activities such as jumping and running may cause excessive traction on the bone causing it to sublux.
- Altered Foot Biomechanics – Most people suffering from cuboid subluxation have flat feet.
Symptoms
A common symptom of cuboid syndrome is pain along the outside of the foot which can be felt in the ankle and toes. This pain may create walking difficulties and may cause those with the condition to walk with a limp.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of cuboid syndrome is often difficult, and it is often misdiagnosed. X-rays, MRIs and CT scans often fail to properly show the cuboid subluxation. Although there isn’t a specific test used to diagnose cuboid syndrome, your podiatrist will usually check if pain is felt while pressing firmly on the cuboid bone of your foot.
Treatment
Just as the range of causes varies widely, so do treatments. Some more common treatments are ice therapy, rest, exercise, taping, and orthotics.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our offices located in Glen Burnie and Ellicott City, MD . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Blog Archives
- 2026
- 2025
- 2024
- 2018